Recent Posts
Archives
15 AWS Innovations That’ll Make Your 2026 Roadmap Fire
Introduction
The cloud landscape is about to shift — again. The 2025 edition of Amazon Web Services (AWS) re:Invent conference delivered one of the most ambitious waves of new services yet — spanning advanced AI, next-gen compute, serverless innovation, storage breakthroughs, and modernization tools.
For organizations planning cloud or AI strategies in 2026, these are not incremental updates — many represent paradigm shifts in scalability, cost, flexibility, and AI adoption. But with new power comes complexity: each service has trade-offs and requires careful evaluation.
In this guide, I unpack the top 15 releases — what they really are, what they give you, where they fall short, which industries stand to benefit most, and concrete use cases (with rough cost/pricing examples).
Let’s dive deep.
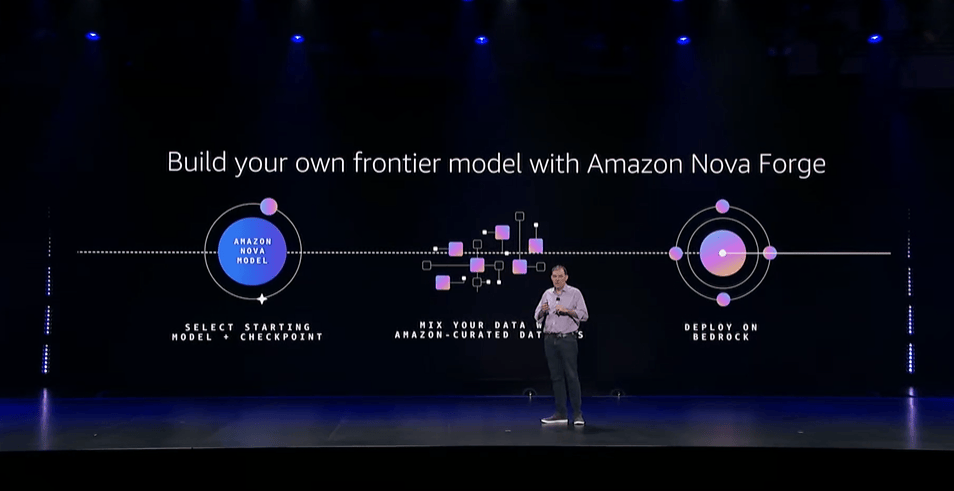
1. Amazon Nova Forge
What it is
Nova Forge is AWS’s new “open-training” platform: enterprises can take a base/foundation model from AWS’s Nova family and use their own proprietary data (or mixture of data) to pre-train, mid-train, or fine-tune these models — producing a custom “Novella” model tailored to their domain. This gives organizations frontier-scale AI power without building everything from scratch.
Advantages
- Domain-specific accuracy: By training on your own data, the resulting model better understands your business terminology, workflows, and compliance context.
- Cost-efficient vs building from scratch: Building a frontier model independently (compute + data + expertise) can cost millions. Nova Forge lowers the barrier to entry.
- Integration with AWS ecosystem: Once trained, models can be deployed via AWS managed services (e.g., Bedrock), benefiting from AWS’s infrastructure, security, and scaling.
Disadvantages / Considerations
- Premium pricing tier: Early reporting suggests enterprise-level costing (e.g., in the ballpark of ~$100,000/year for license/training) — may be prohibitively expensive for small firms or early-stage startups.
- Data governance & compliance risks: Training on proprietary or sensitive data (e.g., PII, medical, financial) demands strong data handling policies, encryption, access control, and compliance oversight.
Need for data readiness: The value depends heavily on the quality, volume, and structure of training data; messy or inconsistent data may yield poor performance.
Industries that benefit
Finance & banking (custom risk, fraud detection, underwriting)
Healthcare and life sciences (medical text/image models, clinical summarization)
Legal / compliance (contract analysis, regulatory summarization)
Enterprise software vendors with vertical-specific needs
Use Case
A mid-sized insurance company wants a model that can read and interpret decades of underwriting, claims, and policy documents — including proprietary codes, clauses, and domain-specific language. Using Nova Forge, they train a custom “underwriting assistant.” That assistant can then analyze new claims, suggest risk scores, or flag suspicious policies, drastically reducing manual overhead and improving consistency.
Rough Pricing Example
- Base license/training: ~US$100,000/year — for initial model build & hosting (as per initial AWS disclosures).
- Ongoing inference and fine-tuning depend on usage volume.
👉 Click here to learn more about Nova Forge
2. Amazon Nova 2 (Sonic / Lite / Omni / Multimodal)
What it is
Nova 2 is AWS’s next-gen family of foundation models, spanning different tiers (Lite, Sonic, Omni) for various workloads: reasoning, multimodal (text, image, video, speech), and speech-to-speech. Sonic aims at conversational AI, including real-time voice interactions; Lite is optimized for cost-effective reasoning + long context (million-token windows); Omni offers multimodal reasoning (text, images, audio, video).
Advantages
Flexible tiers for different use cases: Smaller tasks — use Lite; multimodal or voice interactions — use Sonic or Omni. Reduces cost overhead.
High context-length capacity: Long context windows make them ideal for large documents, long conversations, or multimodal content understanding.
Unified APIs and AWS integration: Easy to plug into Bedrock, other AWS services — no need to manage model hosting yourself.
Disadvantages / Considerations
Potential latency or cost for heavy workloads: Using large models at high volume can become expensive, especially for real-time or high-throughput tasks.
Multimodal risks: For image/video/speech models — risk of hallucinations, content moderation challenges, biased outputs, and unexpected behaviors.
Less control over fine-grained customizations (compared to Nova Forge): If you need domain-specific knowledge, foundation models might underperform without fine-tuning.
Industries that benefit
Customer support centers (multilingual speech bots)
E-commerce/retail (voice-driven shopping assistants, multimodal search)
Media & entertainment (content tagging, summarization, editing)
Education and online learning (interactive tutors, multimodal learning aids)
Use Case
An e-commerce platform integrates Nova 2 Sonic to build a multilingual voice-based shopping assistant: customers speak their requirements (“I want a red dress under $100, size M”), the assistant searches the catalog, shows images, and can respond via voice — improving accessibility and customer engagement, especially in markets where typing is less common.
Pricing Example
Assuming moderate usage (e.g., 10 million tokens/month across various sessions + occasional multimodal processing): US$200 – US$600 / month (depending on model size and usage), before fine-tuning costs.
👉 Click here to learn more about Amazon Nova 2
3. Amazon Bedrock Upgrades + Model Expansion
What it is
Bedrock — AWS’s managed service for foundation models — has been expanded significantly. The 2025 update adds 18 new open-weight models (from providers like Mistral, NVIDIA, and OpenAI-partners), increasing flexibility. It also adds better orchestration and fine-tuning capabilities, making it easier to test multiple models or switch providers without re-architecting infrastructure.
Advantages
Wide model choice: Gives you access to multiple top-tier foundation models — pick the best for your workload without switching clouds.
No infrastructure management: AWS handles hosting, scaling, updates — you use simple APIs.
Simplified experimentation and deployment: Easier to prototype with one model, then shift to another as your needs evolve.
Disadvantages / Considerations
Potential vendor lock-in if you build heavily around Bedrock’s APIs.
Cost scaling: As usage and volume grow, costs can escalate depending on the model and usage frequency.
Privacy and compliance constraints when using third-party models — especially if handling sensitive data.
Industries that benefit
SaaS companies building generative-AI features
Customer support & chatbots
Marketing & content automation
Analytics & data-driven decision platforms
Use Case
A SaaS product for marketing teams uses Bedrock to give users a “smart copywriting assistant” — generating ad copy, blog drafts, and social media posts. If one model’s style doesn’t fit, they can easily switch to another (e.g., Mistral vs OpenAI-partner) to test for the best fit.
Pricing Example
Fine-tuning a small-to-mid model: US$3,000 – US$10,000 (project-based)
Inference & production usage: depends on request volume — starting low, rising with scale
👉 Click here to learn more about Bedrock model expansion
4. Amazon S3 Vectors
What it is
S3 Vectors is AWS’s new native vector storage and retrieval system: instead of using a specialized external vector database, you store embeddings (vectors) directly in a special S3 vector bucket, and use AWS-provided APIs to query them — supporting semantic search, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), vector-based recommendation, and AI retrieval workloads.
Advantages
Cost-effective storage for embeddings — AWS claims up to 90% savings vs dedicated vector databases.
Unlimited scale (within S3 limits) — billions of vectors per index, thousands of indexes per bucket.
No infrastructure to manage — inheriting S3’s durability, availability, encryption, and scalability.
Integration with other AWS AI services — works natively with Bedrock Knowledge Bases, SageMaker, and OpenSearch, making RAG pipelines simpler.
Disadvantages / Considerations
Not a fully-featured vector DB — lacks advanced ANN indexing (HNSW, IVF, etc.) out-of-the-box; more suitable for cold storage, RAG, or lower QPS workloads rather than high-performance, high-QPS similarity search.
Latency trade-offs — While S3 Vectors offers sub-second to ~100 ms queries (depending on load), it may not be ideal for extremely latency-sensitive real-time applications.
You may still need external caching or a hybrid vector DB for high-throughput, low-latency workloads.
Industries that benefit
E-commerce (semantic product search, recommendation)
Media & entertainment (similarity search across large media archives)
Document-heavy businesses (legal, compliance, research) for semantic retrieval / RAG
SaaS products needing embedded storage without heavy infrastructure overhead
Use Case
An e-commerce platform generates embeddings for every product description, reviews, and user behavior. They store these embeddings in S3 Vectors. When a user performs a semantic search (“red leather jacket, size large, affordable”), the system retrieves top matching embeddings and returns relevant products. This enables low-cost semantic search without provisioning or managing a specialized vector database cluster.
Pricing Example
Storing 20 million vectors (~1 KB/vector) → Storage cost + vector queries: Apple estimates around US$100–150/month.
Compared to a standalone vector DB, this can be 4–8× cheaper for storage-heavy, cold-access workloads.
👉 Click here to learn more about S3 Vectors
5. AWS Graviton5
What it is
Graviton5 is AWS’s next-generation custom CPU — powering a new generation of EC2 instances (e.g., M9g) — built on advanced 3nm chip technology, designed for high-performance workloads, energy efficiency, and density. At re:Invent 2025, AWS emphasized Graviton5’s role in giving better price/performance and sustainable compute to customers.
Advantages
High compute density: Graviton5-based instances deliver up to 192 cores per chip and a much larger L3 cache (5× previous generation), which improves per-core performance and consistency.
Better price/performance: For compute-heavy workloads (microservices, batch, high-throughput tasks), Graviton5 can significantly reduce compute cost compared to x86.
Energy efficiency & sustainability: More efficient chips help meet organizational sustainability goals — important for large-scale deployments.
Disadvantages / Considerations
Compatibility issues: Some legacy applications or commercial software may rely on x86-specific binaries; migrating to ARM-based Graviton5 may require recompilation or re-testing.
Ecosystem maturity: While AWS is pushing ARM heavily, certain frameworks, vendor tools, or libraries may still lag.
Not ideal for every workload — high single-thread, latency-sensitive workloads might still favor specialized long-running or GPU-based compute.
Industries that benefit
SaaS companies with a microservices architecture
High-scale web services/backend API providers
Big data processing, analytics jobs, batch workloads
Any cloud-native application built for scale
Use Case
A SaaS product with stateless microservices migrates 70% of its backend services to Graviton5-based instances. The result: compute cost drops by ~30-40%, server density increases, and as they scale up, the cost savings compound — while also reducing energy consumption and improving sustainability metrics.
Pricing Example
New Graviton5 EC2 (M9g or similar) instances are expected to start around US$0.15 – 0.30/hr, depending on size, representing a lower hourly bill compared to older x86-based instances for similar compute power.
👉 Click here to learn more about Graviton5
6. Trainium3 UltraServers
What it is
Trainium3 UltraServers are AWS’s newest AI training servers — built around their third-generation Trainium chips. These servers pack large numbers of chips into a single system, offering very high throughput, lower energy consumption, and optimized training performance for large-scale models. AWS claims up to 3–4× performance improvement over prior generation, with higher energy efficiency.
Advantages
High training performance: Training large models (e.g., billion-parameter LLMs) becomes faster and more cost-efficient.
Energy & cost efficiency: Lower power consumption, lower cost per training run vs GPU-based infrastructure.
Scalable infrastructure under AWS management: No need to build your own on-prem ML server farms; AWS hosts and manages infra.
Disadvantages / Considerations
Still enterprise-grade commitment: Such servers make sense mainly for large models — small/medium ML teams may not use the full potential.
Potential wait times/availability constraints at launch (demand likely high).
Expertise required: Training large models effectively needs skilled ML/DevOps engineers; not plug-and-play.
Industries that benefit
AI-first startups building custom LLMs or generative AI models
Research labs and universities are working on large models
Enterprises building in-house LLMs for internal tools (knowledge management, document search, compliance, etc.)
Media/generative content companies (video, image, voice generation)
Use Case
An AI startup wants to build a custom 50B-parameter model tailored to legal-domain document summarization and contract analysis. Using Trainium3 UltraServers, they run full-scale training in days instead of months, drastically reducing time-to-market and lowering infrastructure costs compared to self-hosted GPU clusters.
Pricing Example
For example: 8 UltraServers running a 2-week training run — approximate cost US$50,000 – 60,000 (hardware + compute + storage), depending on exact usage.
👉 Click here to learn more about Trainium3 UltraServers
7. AWS AI Factories
What it is
AI Factories is AWS’s offering to deliver managed AI infrastructure into customers’ own data centers (on-prem/hybrid) — combining AWS’s AI compute (Trainium, GPU if needed), networking, and services like Bedrock or SageMaker, to give enterprises full control over data residency, latency, compliance, or regulatory requirements.
Advantages
Data residency & compliance control: Sensitive workloads (healthcare, finance, government) can run on-prem while using AWS AI tools.
Low latency for critical applications: Useful for real-time inference where network latency to the cloud is a concern.
Hybrid-cloud flexibility: Enterprises don’t need to fully migrate to the cloud, can keep legacy infra while leveraging modern AI compute.
Disadvantages / Considerations
Initial deployment complexity: Requires data center resources, power, cooling, and integration — not as simple as pure cloud.
Higher upfront commitment: For many enterprises, on-prem infrastructure setup, maintenance, and compliance management still add overhead.
Operational management required: On-prem hardware still needs patching, monitoring, and maintenance.
Industries that benefit
Healthcare (PHI / HIPAA / regulated data)
Government/defense (data sovereignty)
Finance/banking (sensitive financial data)
Enterprises with legacy on-prem systems needing AI acceleration
Use Case
A large hospital network chooses AI Factories to host an on-prem AI inference system for medical imaging analysis (radiology, pathology). The system processes images locally to ensure compliance and privacy, while non-sensitive metadata gets aggregated to the cloud for analytics and reporting — giving the best of both worlds.
Pricing Example (Illustrative)
Setting up an AI Factory cluster: US$250,000 – 1,000,000 annually, depending on scale, hardware mix (Trainium vs GPU), power/cooling infrastructure, and usage.
👉 Click here to learn more about AI Factories
8. AWS Lambda Durable Functions & Lambda Managed Instances
What it is
Lambda Managed Instances allow Lambda functions to run on EC2 compute — giving access to specialized hardware or dedicated instances while retaining serverless ease. Durable Functions give Lambda the ability to orchestrate long-running, stateful workflows (from seconds to up to one year), with reliability and auto-scaling built in.
Advantages
Serverless simplicity + compute flexibility: Use a serverless model for manageability, but with the power of EC2 hardware beneath.
Long-running workflows support: Useful for tasks that involve human approval, external events, or delayed processing, without paying for idle resources constantly.
Cost-efficient orchestration: Instead of provisioning full servers for sporadic workloads, pay only when tasks are active.
Disadvantages / Considerations
Potential higher cost vs simple Lambdas: For heavy compute or long-running tasks, cost trade-offs must be evaluated.
Added complexity in workflow design: Orchestrating durable, stateful workflows requires careful design (time-outs, error handling, orchestration logic).
Observability and debugging: Long workflows may be harder to monitor, especially when they depend on multiple external triggers or asynchronous events.
Industries that benefit
IoT (device updates, firmware rollouts, sensor data processing)
Logistics & supply chain (multi-step shipments, event-based workflows)
Financial services (batch processing, scheduled jobs, overnight processing)
Enterprises migrating legacy cron jobs to cloud-native workflows
Use Case
An IoT manufacturer leverages Durable Functions to manage firmware update rollouts across thousands of devices. The workflow includes: schedule rollout → wait for each device’s availability → push update → verify report → handle failures. Because the workflow may take days or weeks across many devices, Durable Functions handle orchestration without needing always-on servers — cost and complexity are reduced substantially.
Pricing Example
Assuming ~1 million function-hours per month (active workflows + idle wait time): US$3,000 – $7,000/month (varies with compute and memory configuration).
👉 Click here to learn more about Lambda Durable Functions & Managed Instances
9. Amazon EKS Capabilities (2026 Enhancements)
What it is
EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service) now includes enhanced orchestration and cloud resource management capabilities — simplifying workload orchestration, scaling, security, and policy management for containerized applications on AWS.
Advantages
Reduced operational overhead: AWS handles more of the Kubernetes lifecycle — upgrades, scaling, networking, etc.
Better enterprise-grade reliability & governance: Consistent policies across clusters, improved security configurations, easier multi-cluster management.
Faster developer velocity: Teams can focus on application logic instead of infra management.
Disadvantages / Considerations
Not trivial for small teams: For small deployments, Kubernetes + EKS might be overkill compared to simpler container or serverless setups.
Learning curve: Teams unfamiliar with container orchestration, microservices, and Kubernetes need ramp-up time.
Cost overhead: Running multiple clusters or high-availability setups increases cost compared to simpler services.
Industries that benefit
SaaS and platform companies using microservices and containers
Organizations with multi-region deployments or compliance/isolation needs
Enterprises moving from monolithic apps to container-based architectures
Use Case
A software vendor with multiple microservices deploys onto EKS. With the new EKS Capabilities, they standardize cluster policies (security, resource limits), orchestrate auto-scaling based on load, and simplify deployments — reducing operational toil and improving reliability as they scale globally.
Pricing Example
EKS cluster overhead: ~US$0.10 / hr per cluster, plus node instance costs — good for medium-to-large container workloads.
👉 Click here to learn more about EKS Capabilities
10. AWS Database Savings Plans + RDS / DB Enhancements
What it is
Database Savings Plans introduce a flexible pricing model across AWS-managed database services (RDS, DocumentDB, etc.) — offering discounts in return for consistent usage commitment. Additionally, AWS expanded features for SQL Server/Oracle, improved storage limits, and optimized database scaling and management.
Advantages
Predictable cost savings: Up to ~35% (or more, depending on plan) discount compared to on-demand DB usage — helpful for budget planning.
Flexibility across DB engines: Works across multiple DB services, making it easier if you use various database technologies.
Better scalability and management features: New instance support, larger storage options, and optimized performance for large workloads.
Disadvantages / Considerations
Requires commitment and usage forecasting: If usage drops drastically, savings might not offset commitment.
Less suitable for fluctuating workloads: Highly variable DB workloads may not benefit as much.
Still managed — limited control: Less control over lower-level DB infrastructure compared to self-managed DBs.
Industries that benefit
SaaS platforms with predictable, steady database usage
Fintech, e-commerce, subscription-based services
Enterprises moving from on-prem to managed DBs to reduce DB-ops overhead
Use Case
A subscription-based SaaS company using PostgreSQL on RDS opts into the Database Savings Plan. Given predictable monthly DB usage, they secure a ~30% discount — lowering recurring costs and making long-term financial forecasting easier.
Pricing Example
For a mid-size RDS PostgreSQL cluster with steady usage: 20–50% discount vs on-demand — savings vary based on plan and commitment.
👉 Click here to learn more about Database Savings Plans
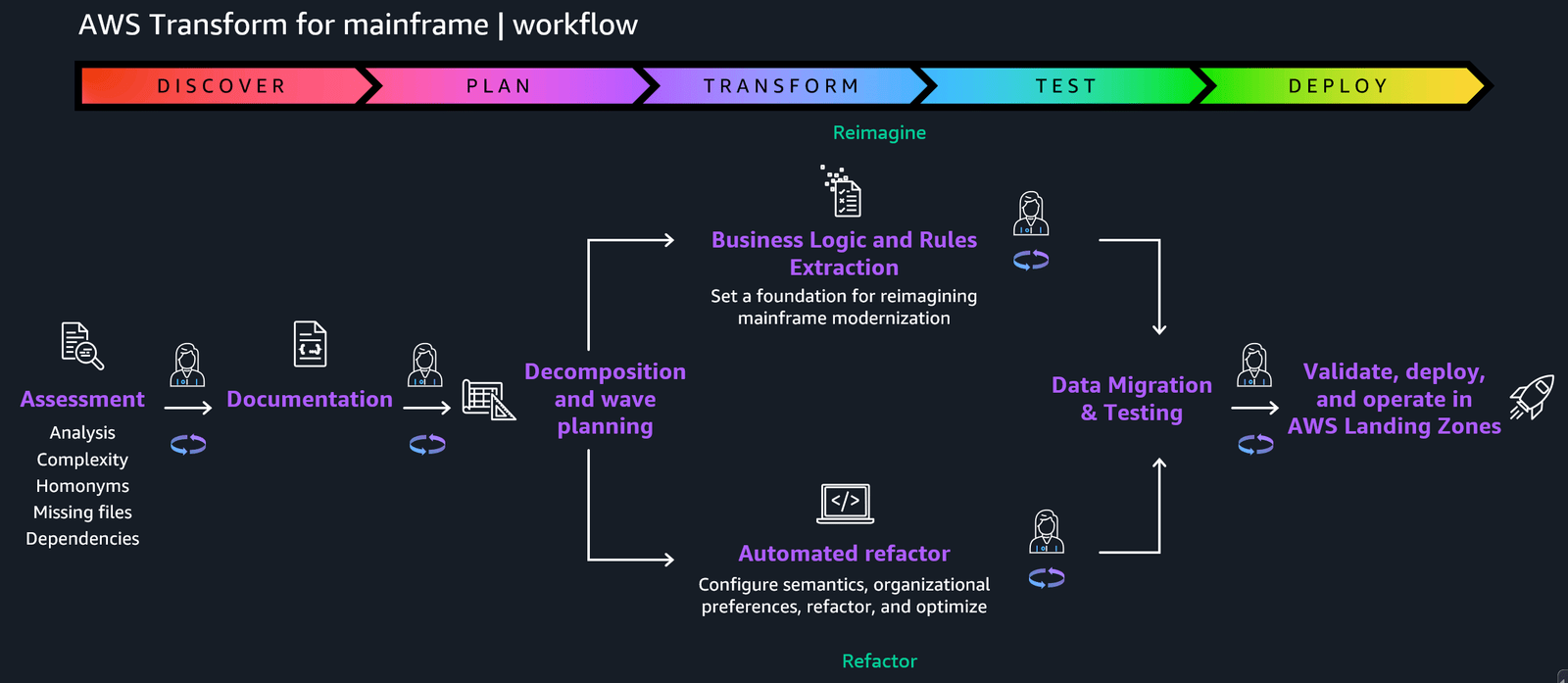
11. AWS Transform (Custom & Legacy Modernization)
What it is
AWS Transform is a new AI-powered service designed to modernize legacy applications (including Windows, .NET, mainframe, and older databases) by automatically analyzing old codebases, refactoring or rewriting them, updating deployment configurations, and even automating tests — drastically reducing time and cost compared to manual rewrites.
Advantages
Significant time savings: Migrating legacy monolithic or mainframe apps to cloud-native or microservices is up to 5× faster than manual rewriting.
Reduced technical debt: Helps organizations modernize legacy infrastructure without starting from scratch — preserving business logic while enabling modern cloud deployment.
Automated testing and deployment support: Helps reduce errors commonly introduced during manual rewrites.
Disadvantages / Considerations
Potential inaccuracies / missed edge cases: Automatic transformations may miss complex business logic or corner-case handling — manual review still needed.
Requires detailed testing & validation post-conversion — cannot assume 100% correctness automatically.
It may not be suitable for extremely customized or obscure legacy systems with heavy dependencies or proprietary modules.
Industries that benefit
Banking & insurance (traditional core banking/claims systems)
Government agencies & public sector (legacy mainframe or Windows systems)
Enterprises with legacy ERP / CRM / custom in-house software
Any firm looking to reduce licensing or maintenance costs for old software
Use Case
A large insurance company with a decades-old COBOL mainframe claims processing system uses AWS Transform to migrate to a microservices architecture. They convert business logic, data access layers, and backend services, enabling modern cloud-based deployment — cutting maintenance costs, improving scalability, and decoupling old dependencies.
Pricing Example
Modernizing a 1M-line legacy codebase: US$100,000 – 750,000 depending on complexity, number of modules, and degree of customization.
👉 Click here to learn more about AWS Transform
12. AWS Interconnect (Multi-cloud) (Preview)

What it is
AWS Interconnect (multicloud preview) is a new networking offering that enables private, high-speed, low-latency connectivity between AWS and other cloud providers — facilitating hybrid- or multi-cloud architectures, data exchange, and disaster recovery setups.
Advantages
Secure, private connectivity across clouds — avoids public internet, reducing latency and improving security.
Hybrid & multi-cloud designs supported — ideal for enterprises needing redundancy, regulatory compliance, or global distribution.
Better disaster recovery and failover capabilities — easier to replicate data and services across clouds.
Disadvantages / Considerations
Currently in preview — may have limited availability and potential for changes.
Complex network architecture and configuration required — planning, routing, failover mechanisms, and compliance need careful setup.
Potential cost and vendor management overhead — using multiple clouds entails complexity in billing, monitoring, and cross-cloud orchestration.
Industries that benefit
Global enterprises with presence in multiple regions/cloud providers
Retail, e-commerce — requiring high availability and global coverage
Regulated industries needing redundancy, compliance, or data residency across regions
Use Case
A global retailer uses AWS for backend services but leverages another cloud for some specialized services (e.g., video processing, data analytics). With AWS Interconnect, they set up private links between AWS and the second cloud — enabling low-latency data replication, unified failover, and consistent global user experience.
Pricing Example (Preview/Speculative)
Private interconnect link (multi-cloud): US$2,000 – 10,000/month, depending on bandwidth, data transfer, and redundancy needs.
👉 Click here to learn more about AWS Interconnect (Multi-cloud)
13. AWS DevOps Agent (Preview)

What it is
DevOps Agent is AWS’s new AI-powered tool designed to act as an autonomous “on-call engineer”: it analyzes telemetry from CloudWatch, GitHub, ServiceNow (or other monitoring tools), identifies root causes, suggests resolutions or playbooks, and can coordinate incident response — helping reduce mean time to recovery (MTTR) and manual on-call load.
Advantages
Faster incident detection & triage — automation reduces human overhead and speeds up response.
Consistent root-cause analysis and recommendations — reduces dependency on individual engineers’ experience.
Scalable incident management — useful for large infrastructure footprints with many services.
Disadvantages / Considerations
Accuracy and trust issues: AI-driven root cause detection may misclassify or miss issues — must be reviewed.
Dependency on telemetry and monitoring setup: Without robust observability (metrics, logs, alerts), agent effectiveness is limited.
Need for fallback and human oversight — cannot fully replace human engineers, especially for complex incidents.
Industries that benefit
SaaS and web services companies with high availability requirements
E-commerce, fintech — where downtime or outages have a big financial impact
Enterprises with large, distributed microservice architectures
Use Case
A SaaS startup integrates DevOps Agent into its pipeline: when spikes or errors occur (e.g., during deployments or traffic surges), the agent automatically runs diagnostics, suggests remediation steps, and alerts engineers with structured reports — reducing manual on-call load and slashing MTTR by up to 50%.
Pricing Example
Typical usage: US$5 per 1,000 events, the monthly cost could range from US$50 – 500, depending on the volume of incidents and telemetry events.
👉 Click here to learn more about DevOps Agent
14. AWS Security Agent + Security Enhancements
What it is
Security Agent (alongside upgrades to GuardDuty, Security Hub, IAM Policy Autopilot) is AWS’s push into AI-driven security and AppSec: automated code-review, policy generation, threat detection, real-time risk analytics, and simplified least-privilege enforcement.
Advantages
Automated security baseline enforcement — reduces human error, speeds up secure deployments.
Continuous monitoring and threat detection across VM, container, and serverless infrastructure — helps detect complex, multi-stage attacks.
IAM policy automation — simplifies fine-grained permissions based on actual application behavior, reducing the risk of over-privileged access.
Disadvantages / Considerations
False positives or over-restrictiveness — automated tools may flag benign behavior or block legitimate workflows.
Need for tuning and context-awareness — effective usage requires tuning thresholds, whitelisting, and understanding false-positive patterns.
May miss domain-specific security nuances — automatic policy generation might not cover all regulatory or business-specific compliance requirements.
Industries that benefit
Finance, banking, fintech (high compliance, high-security needs)
Healthcare (PHI handling, HIPAA, data privacy)
E-commerce, SaaS — especially multi-tenant platforms, SaaS with external integrations
Use Case
A fintech company uses AWS Security Agent + IAM Policy Autopilot to auto-generate least-privileged access policies for new microservices. Each time a service is deployed, IAM roles are generated based on observed behavior — reducing security risk and eliminating manual policy writing.
Pricing Example
Security monitoring & events: US$0.001 – 0.005 per event; monthly cost around US$30 – 800 depending on scale and event volume.
👉 Click here to learn more about AWS Security Agent & enhancements
15. Amazon S3 Tables + Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP + Storage Enhancements
What it is
AWS expanded S3, FSx, and S3 Tables features for improved storage flexibility, data lake capabilities, replication, intelligent-tiering, and unified analytics/storage workflows. Includes easier integration between object storage (S3), file systems (FSx), and data-table layers (S3 Tables).
Advantages
Unified storage + analytics stack: Store raw files (media, logs, datasets) in FSx or S3, index metadata in S3 Tables — easy to query, analyze, and manage.
Cost optimization via Intelligent Tiering & Replication: Automatically move cold data to cheaper storage tiers and replicate across regions/accounts for DR/compliance.
Simplifies data pipelines for ML, analytics, media: No need for external storage solutions — all within the AWS ecosystem.
Disadvantages / Considerations
Application architecture changes may be required: To fully leverage new storage/analytics features, some refactoring might be needed.
Replication and storage costs: While tiering helps, large-scale storage and multi-region replication still incur costs, not free.
Learning curve for data lake + table-based workflows: Teams need to adopt metadata management, table schemas, partitioning, and lifecycle policies.
Industries that benefit
Media & entertainment — video/audio storage + metadata indexing + analytics
Data analytics/data warehouses/data lakes — large-scale logs, analytics data, ML datasets
Life sciences/research — storing large datasets (genomics, imaging) and querying metadata/results
Enterprises migrating legacy file systems to cloud-native storage + analytics
Use Case
A video-streaming company stores all raw video footage and user-uploaded media in FSx, uses S3 to store processed clips, and utilizes S3 Tables to manage metadata, usage analytics, and indexing. Intelligent-tiering moves rarely-accessed assets to cheaper storage, while replication ensures backup across regions — reducing cost and improving reliability.
Pricing Example
Combined FSx + S3 + S3 Tables: US$50 – 500/month depending on storage size, access frequency, and replication settings.
👉 Click here to learn more about S3/FSx/S3 Tables enhancements
Strategic Recommendations: What to Pilot in 2026
Start small with vector-based AI → If you’re experimenting with semantic search or AI retrieval, adopt S3 Vectors + Nova 2 as a low-cost, low-infra-overhead starting point.
Modernize legacy systems wisely → Use AWS Transform to migrate older apps, but invest in thorough testing and validation.
Plan AI infrastructure carefully → For heavy AI workloads, evaluate Trainium3 or AI Factories; for standard web services, consider Graviton5 for cost/performance optimization.
Use serverless whenever possible → Durable Functions + Lambda Managed Instances let you orchestrate complex workflows without overprovisioning.
Prioritize security from day one → Adopt Security Agent / GuardDuty enhancements and IAM Policy Autopilot if you’re handling sensitive data or operating under compliance requirements.
Final Thoughts
2026 looks like the year when AWS turns from “cloud provider” to a comprehensive AI + data + compute + infrastructure platform. The breadth and depth of re:Invent 2025 innovations show AWS is betting big on hybrid workloads — from legacy modernization to next-gen AI — and providing tools that can scale from small startups to global enterprises.
But power comes with responsibility, complexity, security, cost management, and data governance — all must be handled carefully.
If you’re looking to adopt any of these services, build a roadmap, or run a cost-benefit analysis — I’m here to help.
👉 Reach out to me anytime for architecture guidance, pricing estimates, or strategic AWS adoption plans.